The rise of e-commerce has led to a greater assortment of shops. In addition, the internet has greatly increased price transparency in the market, which in turn has increased the frequency of price changes.
The combination of these two factors made dynamic pricing a necessity in today’s retail market. And as part of the Five Steps to Successfully Implement Dynamic Pricing, shops need to choose a pricing method that makes sense for their organization.
Dynamic pricing is often equated with a purely competitor-based pricing method. For example, “Always adjust the price to the lowest of the three competitors X, Y and Z”. Competitor-based pricing, however, isn’t the only dynamic pricing method, nor is it the most recommended pricing method. Three dynamic pricing methods are outlined in this blog post.
Pricing method 1: Cost-plus
The most straight-forward pricing method is cost-plus pricing. The starting point is the cost per product, where the desired margin (percentage or € amount) is added to calculate a selling price. If the cost per product changes daily or even hourly (due to changing suppliers or dropped shipping for example), it is necessary to implement this method dynamically.

- Main advantage: Easy to understand & implement
- Main disadvantage: Takes only internal factors into account
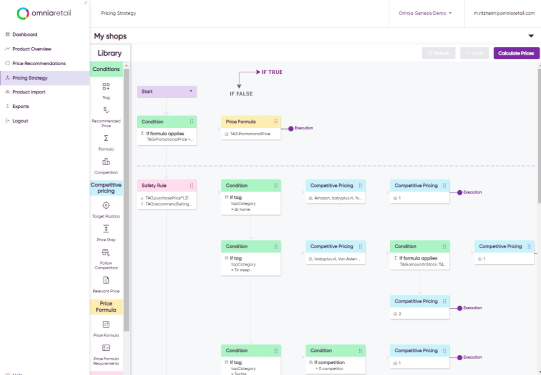
How can I apply the cost-plus pricing method in Omnia?
This method is easily implemented in Omnia. Create a new variable with the formula editor. Start with the purchase price and add all other product costs from your feed plus a desired margin, possibly at the product-level. Include this variable in your strategy settings as a lower & upper limit and you are set.
Read more: The Ultimate Guide to Dynamic Pricing
Pricing method 2: Competitor-based
With competitor-based pricing, products are priced relative to (direct) competition. For instance, a company might want to undercut a certain competitor. Or, a company might want to maintain a certain price position in the market.
It is a common strategy for shops to match prices with their most important competitors for certain products. Stores specialized in electronic products have the highest frequency of price changes and other product categories are likely to follow with an increasing frequency. Therefore, it is essential to implement this method dynamically to not lose any market share.

- Main advantage: Takes external factors (competitors) into account
- Main disadvantage: Assumes your competitors have the right price
How can I apply competitor-based pricing method in Omnia?
Two steps are involved to implement this method in Omnia:
1. Create an action, which is the concrete formalization of your strategy. Some examples:
- Never price higher than competitor X
- Never price lower than position 2 in the market
- Set price equal to most occurring price
- Etc.
2. Apply this action in the Strategy settings within Omnia to a part of your assortment based on a variable, such as: brand, category, color or even stock. An example: raise price above the average of the market when stock is below 10.
Pricing method 3: Value-based
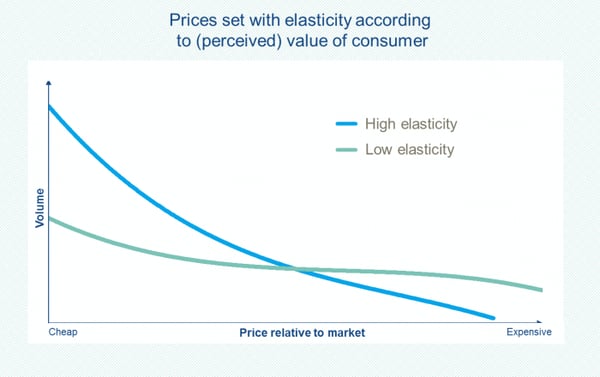
By far, the most recommended pricing method by experts is value-based. Value-based pricing is a dynamic pricing method based on the economic principles of demand and shows the best results in additional sales and total margin. As the true value of products is difficult to uncover, consumers’ willingness-to-pay functions as a proxy for the perceived value.
Omnia calculates the price elasticity of products to uncover consumers’ willingness-to-pay for the combination of product and seller. A product with high price elasticity is very sensitive to price changes as consumers value the product less than a product with low elasticity (keeping all other things equal).
Over time, Omnia learns how much consumers are willing to pay for the product at each price point relative to the competition. You can use this data to further optimize your pricing strategy and create rules for maximum profit with the given price elasticity.
- Main advantage: Combines external and internal data
- Main disadvantage: Most complicated pricing method
How can I apply this method in Omnia?
After a few months of gathering sales data and comparing prices against those of the competitors, Omnia has sufficient data to determine the price elasticity of products and categories. You can then use those insights to build pricing rules that capitalize on the price elasticities of different products or categories.
Ending remarks
While value-based pricing in theory is the best pricing method, Omnia recognizes the importance of having complete flexibility in automating pricing strategies. Omnia gives the power to (online) retailers to use all three popular pricing methods at the product level and even combine them according to your strategy. For example, the strategy in Omnia for a specific product could be:
- Begin with value-based pricing through price elasticity
- Never price higher than competitor X
- Never price lower than 10% margin
To conclude, there are five main benefits when you use Omnia’s integrated pricing methods:
- Omnia brings internal product & sales data together with external market & consumer data
- Omnia’s proprietary algorithm automatically determines the price elasticity of products and categories
- Easily combine all three pricing methods at the product level
- Automation of the pricing process, multiple times per day
- No "black box": Omnia is completely transparent about the decisions of the price setting process.
For more information about our dynamic pricing & marketing software or guidance on how to implement these pricing methods, please contact us via info@omniaretail.com or call +31 (0) 35 699 02 22.
Curious to learn about other pricing strategies or interested in our Amazon guide series? Check out some of our other articles below:
- What is Value Based Pricing?: A full overview of how price and consumer perception work together.
- What is Charm Pricing?: A short introduction to a fun pricing method.
- What is Penetration Pricing?: A guide on how to get noticed when first entering a new market.
- What is Odd Even Pricing?: An explanation of the psychology behind different numbers in a price.
- What is Bundle Pricing?: Learn more about the benefits of a bundle pricing strategy.
- What is Cost Plus Pricing?: In this article, we’ll cover cost-plus pricing and show you when it makes sense to use this strategy.
- What is Price Skimming?: Learn how price skimming can help you facilitate a higher return on early investments.
- What is Map Pricing?: Find out why MAP pricing is so important to many retailers.
- Here’s What You Need to Know About Psychological Pricing (Plus 3 Strategies to Help You Succeed): Modern day pricing is so much more than a numbers game. When thought about correctly, it’s a powerful way to build your brand and drive more profits.
- How to Build a Pricing Strategy: A complete guide on how to build a pricing strategy from Omnia partner Johan Maessen, owner of Commercieel Verbeteren.
- The Strategies Behind Amazon's Success: Learn how Amazon became 'the place' to buy products online.
- The Complete Guide To Selling on Amazon: In this guide we answer some of the top questions we hear about Amazon and give helpful hints on how to succeed on the platform.
- How Does Amazon's Search Algorithm Work: Find out how Amazon connects their shoppers with relevant products as quickly as possible.
- Price, The Most Important P in the Marketing Mix: In this article we'll look at the relevance of the 7 P’s in today’s online marketing context.